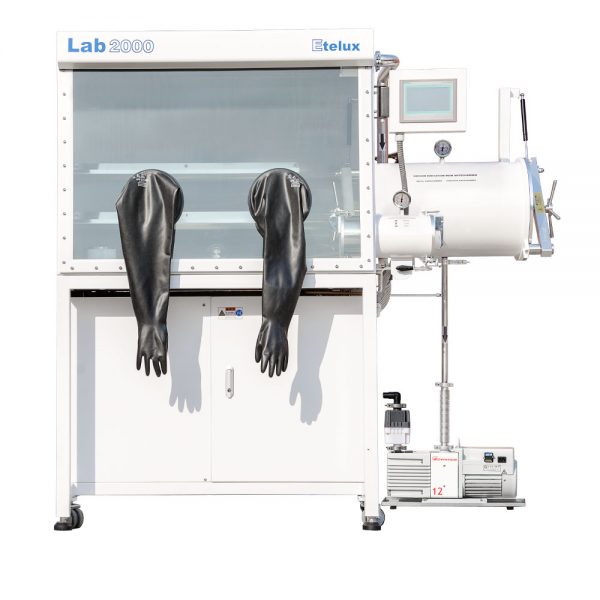
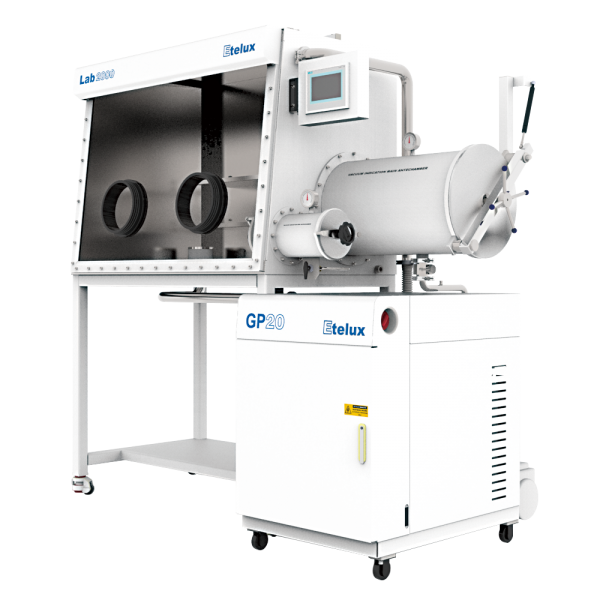
A glove box is a piece of equipment commonly used in scientific research, pharmaceuticals, semiconductor manufacturing, and other fields to provide an environment free of oxygen, water, or other specific atmospheres to protect sensitive materials or experiments from outside conditions. In order to meet the need for temperature control in some experiments or manufacturing processes, gloveboxes are often equipped with a heated transition chamber, a component that can heat materials or tools introduced into the interior of the glovebox under airtight conditions. The following is a detailed description of the glove box transition chamber heating principle, heating method and its considerations in practical applications.
Heating Principle
Heating in a glovebox transition compartment usually relies on built-in heating elements, which can be resistance wires, heating pads, or more advanced heating membranes. The heating element converts electrical energy into thermal energy to raise the temperature in the transition compartment. The heating process requires precise temperature control to avoid damaging sensitive materials or causing deviations in experimental results. Therefore, the heating system is usually connected to a temperature control unit, such as a PID controller (Proportional-Integral-Derivative Controller), for precise regulation of the heating rate and target temperature.
Heating Methods
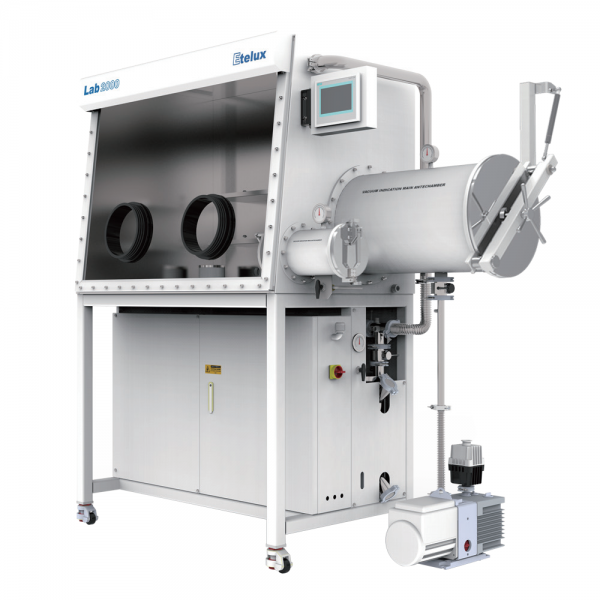

- Direct heating method: The direct heating method means that the heating element is installed directly on the inner wall or the bottom of the glove box transition chamber, and the heat is transferred to the air in the chamber or the placed objects through contact. This method of heating speed, but may cause uneven temperature distribution, requiring good heat transfer design and temperature control strategy. 2. indirect heating method: indirect heating method: indirect heating element is mounted directly on the inner wall or bottom of the glove box transition compartment.
- Indirect heating: Indirect heating may be by hot air circulation or hot liquid circulation. Hot air circulation is by means of a fan that uniformly feeds heated air into the transition chamber, while hot liquid circulation is by means of a heating medium (e.g., oil or a special liquid) circulating in a closed loop and transferring heat to the transition chamber through a heat exchanger. These two methods provide a more uniform temperature field and are suitable for application scenarios that require higher temperature uniformity.
- Radiant Heating: In some special cases, infrared radiant heating technology may be used. This method heats the surface of the object directly through radiant energy, not the air, and is suitable for situations where rapid surface heating is required and where internal temperature control is not critical.
Temperature control and monitoring To ensure the stability and safety of the heating process, the heating system of a glove box transition compartment usually integrates the following key components:
- Temperature sensors: located inside the compartment or close to the heating elements, they monitor temperature changes in real time and feed back to the temperature control unit.
- Controllers: PID controllers, such as those mentioned above, adjust the power output of the heating elements according to the difference between the set point and the actual temperature to maintain a constant temperature in the cabin.
- Safety protection mechanism: including over-temperature protection, power failure protection, etc., in order to prevent the safety risk caused by high temperature or power failure. Practical application considerations
- Material compatibility: When choosing a heating method, the material characteristics should be considered to ensure that the material will not be damaged or chemically reacted due to high temperature.
- Temperature uniformity: For experiments that require precise temperature control, ensure that the heating system provides a uniform temperature field to minimize experimental errors.
- Gas environment: When operating in a specific gas environment, the heating process should also take into account factors such as thermal expansion and chemical stability of the gas.
- Energy consumption and efficiency: Energy efficient heating solutions are particularly important for long term glove box systems, taking into account both cost and performance.
- Maintenance and cleaning: the heating components of the transition chamber should be easy to disassemble and clean to ensure the reliability and safety of long-term use.
In short, the heating design of the glove box transition chamber is a technical challenge that takes into account temperature control accuracy, safety, efficiency and applicability. Through rational selection of heating methods, precise temperature control technology and thorough safety design, it can ensure that the glove box plays its due role in complex experimental and production environments.