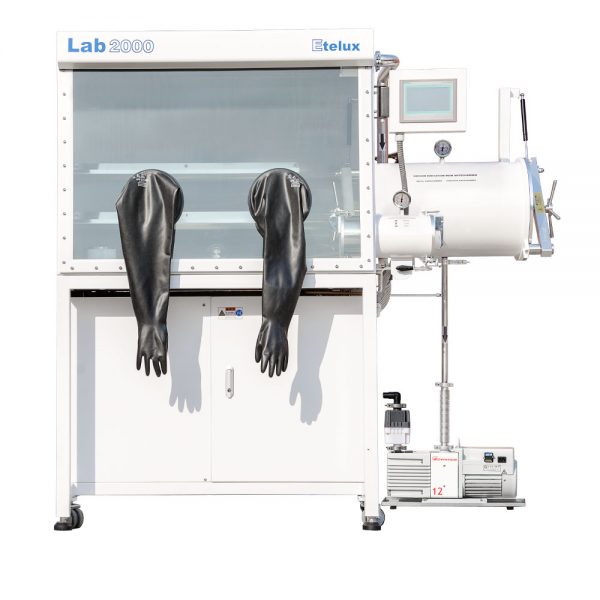
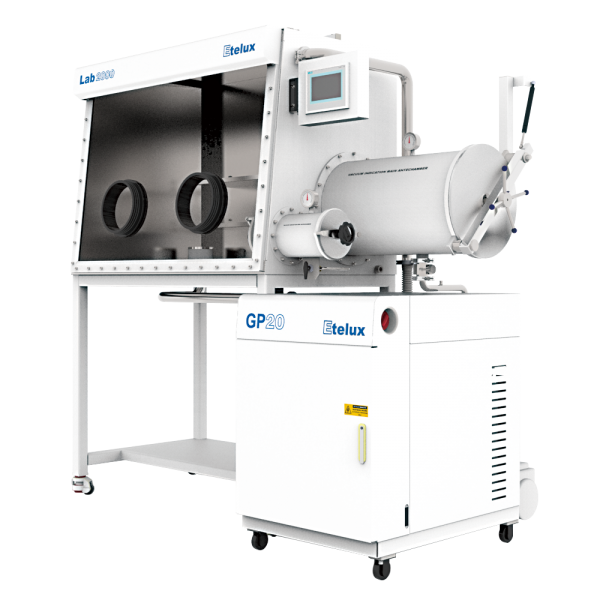
It is crucial to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and instructions specific to the glove box model being used. Following proper maintenance and operational procedures, along with proactive troubleshooting, will help address and mitigate common issues, ensuring the effective functioning of glove boxes and the reliability of experimental or process results.
Here, we discuss some of the frequently encountered issues and the recommended solutions:
- Leakage:
- Issue: Leakage of air or contaminants into the glove box can compromise the controlled environment.
- Solution: Perform regular leak tests using appropriate methods like helium leak detectors. Identify and repair any leaks promptly. Ensure all seals and connections are properly maintained.
- Moisture Build-up:
- Issue: Excessive moisture inside the glove box can affect sensitive samples or processes.
- Solution: Use a dehumidifier or desiccant to control moisture levels. Ensure the glove box is properly sealed and maintain a positive pressure of dry nitrogen. Regularly monitor and maintain the glove box’s gas purification system.
- Oxygen Contamination:
- Issue: High oxygen levels can react with sensitive materials or compromise the integrity of the controlled environment.
- Solution: Monitor oxygen levels using an oxygen analyzer. Maintain a consistent flow of high-purity nitrogen to displace oxygen. Activate and properly maintain the glove box’s gas purification system to remove oxygen from the environment.
- Glove Integrity:
- Issue: Damaged or degraded gloves can lead to contamination or exposure risks.
- Solution: Regularly inspect gloves for any signs of wear, tear, or degradation. Replace damaged gloves promptly. Use proper techniques when handling objects inside the glove box to prevent unnecessary stress on the gloves.
- Temperature Control:
- Issue: Poor temperature control can affect certain experiments or processes.
- Solution: Use a cooling or heating system to control the temperature inside the glove box. Ensure the system is properly calibrated and that the desired temperature range is maintained consistently. Regularly monitor and adjust the temperature as needed.
- Contaminant Control:
- Issue: Introduction of contaminants into the glove box can compromise the integrity and purity of the controlled environment.
- Solution: Implement strict cleanliness protocols. Clean all items and equipment before bringing them inside the glove box. Use proper techniques when transferring materials to minimize the risk of contamination. Regularly clean and maintain the interior surfaces of the glove box.
- Power Interruptions:
- Issue: Unexpected power failures or interruptions can cause disruptions or potential sample damage.
- Solution: Install a backup power supply or uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to ensure continuous power in case of outages. Implement protocols for safely shutting down the glove box during power interruptions to prevent damage.
- User Training and Education:
- Issue: Inadequate user training can result in improper use of the glove box and its features.
- Solution: Provide proper training to all users on the correct operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the glove box. Emphasize the importance of following protocols and safety guidelines to prevent issues and ensure optimal performance.